This feature available on larger devices.
Topics
Expand course material with short, topical videos.
(Click to start)

Topics
Narrow by course topic:
Anatomy
Neuroanatomy
Quick-start cases:
Dural layers
External brain
Brain sections
Base of skull
Cranial nerves
Multiple brain features
How to find more:
Go to the Anatomy Pins page. Search by anatomic term.
Other anatomy
Quick-start cases:
Heart within pericardial sac.
Lungs and airway (posterior view).
Diaphragm
How to find more:
Go to the Body Map. Search under the Anatomy option by body location. The page guides you through.
Or, go to the Anatomy Pins page to search by anatomic term.
Find specific anatomy structures
Quick-start cases:
Papillary muscle with chordae tendinae
Abductor pollicis longus muscle
Ampulla of Vater
How to find more:
Go to the Anatomy Pins page to search by anatomic term.
Anatomic variation
Quick-start cases:
Bifid xyphoid process
Metopic (frontal) suture
Accessory spleen
How to find more:
Go to the Anatomy Variation page.
Pathology
Find any pathology on the site
How to find more:
Search the Library.
Or, search alphabetically in the Anatomy Pins page.
Compare similar conditions across patients
How to find more:
Use the Clinical Panels page to find examples of tumors, heart disease, and other processes in groups of patients.
Clinical Medicine Skills
External Exam – general
Quick-start cases:
External exam – Case 1
External exam – Case 2
External exam – Case 3
External Exam – Specific Findings
Quick-start cases:
Use of symmetry during physical exam.
Abdominal distention.
Debrided decubitus ulcer.
Dried blistering from reperfusion syndrome.
Unilateral leg swelling.
Loss of muscle mass.
History Taking – Symptom description
Quick-start cases:
The patient was diagnosed with musculoskeletal pain, but the origin was cardiac.
The patient had cardiac symptoms, but a negative work-up and then died from hypertensive disease. His coronary arteries were wide open.
The patient had chronic back pain then new onset back pain one week prior to death. The autopsy showed his pacemaker lead ruptured through the septum of the heart.
How to find more:
Review the History. Decide what history-taking skills would apply.
Vital sign – Blood Pressure
Quick-start cases:
The patient had intraoperative hypotension then multiorgan failure. The case illustrates cardiogenic shock (bowel infarct, liver infarct, hepatic vein thrombosis, abnormal labs.)
The patient was hypotensive after dialysis, then died. The blood pressure values from dialysis are provided.
The patient presented with symptomatic hypertension. Then his blood pressure normalized. But it’s because he was in hemorrhagic shock with hemoperitoneum.
Vital sign – Heart rate
Mental Status change
Quick-start cases:
The patient had mental status changes after a spinal surgery. Clinical considerations were medication-related or a central nervous system infection.
The patient had mental status changes after losing a pulse in her foot following an angiogram. The physician diagnosed anxiety and prescribed anxiolytics, but the patient was in hemorrhagic shock.
The patient had mental status changes, with consideration of medication use.
The patient was diagnosed with “sundowning” but had suffered head trauma from a fall.
Kidney failure
Quick-start cases:
The case shows a patient with a peritoneal dialysis catheter and cirrhosis.
The patient was a dialysis patient with chronic renal failure.
The patient had new onset kidney failure presenting with a “metallic taste” taste in his mouth.
The patient had acute renal failure. The case illustrates weight gain, fluid retention (anasarca) and uremic pericarditis.
The patient had obstructive (post-renal) acute kidney failure from an enlarged prostate. He presented with severe hypertension and died from hemoperitoneum.
Neurology
Quick-start cases:
The case illustrates a large stroke with cavitation. (Case 20 Part 7).
The physical exam in this case illustrates loss of muscle mass in a patient with immobility.
The case shows cerebral edema, midline shift and duret hemorrhages (related to head trauma from a fall).
Communication,
Relationships, Ethics
Quick-start cases:
-When should a provider ask for help?
-What is the basis of competence?
-How do you talk to families when the loved one becomes sick under their care?
-What is the basis of competence?
-How do you talk to families when the loved one becomes sick under their care?
-What’s the moral obligation to report adverse events?
-Who should be notified?
-Who should be notified?
-Who makes life or death decisions during an emergency?
-What is the provider’s role in providing care to an unstable patient who refuses treatment?
-What is the provider’s role in providing care to an unstable patient who refuses treatment?
-How do you maintain professional integrity when pressured by the family or patient?
-What is the ethics of operating without evidence-based reasoning?
-What is the family’s role in ensuring care?
 Library
Library History
History Panels
Panels
 Case 13 Part 11
Case 13 Part 11 Case 19 Part 5
Case 19 Part 5 Case 19 Part 6
Case 19 Part 6 Case 5 Part 1
Case 5 Part 1 Case 35 Part 2
Case 35 Part 2 Case 17 Part 4
Case 17 Part 4 Case 35 Part 2
Case 35 Part 2 Case 14 Part 5
Case 14 Part 5 Case 13 Part 9
Case 13 Part 9 Case 17 Part 4
Case 17 Part 4 Case 20 Part 4
Case 20 Part 4 Case 42 Part 1
Case 42 Part 1 Case 5 Part 1
Case 5 Part 1 Case 1 Part 1
Case 1 Part 1 Case 2 Part 1
Case 2 Part 1 Case 3 Part 1
Case 3 Part 1 Case 6 Part 1
Case 6 Part 1 Case 10 Part 1
Case 10 Part 1 Case 13 Part 1
Case 13 Part 1 Case 28 Part 1
Case 28 Part 1 Case 29 Part 1
Case 29 Part 1 Case 37 Part 1
Case 37 Part 1 Case 14
Case 14 Case 46
Case 46 Case 8
Case 8 Case 27
Case 27 Case 44
Case 44 Case 39
Case 39 Case 34
Case 34 Case 32
Case 32 Case 43
Case 43 Case 41
Case 41 Case 20
Case 20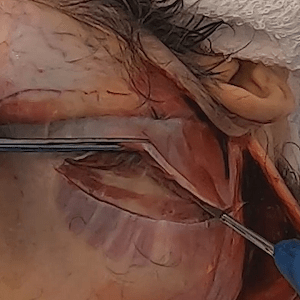 Case 43
Case 43 Case 11
Case 11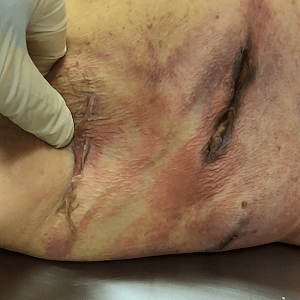 Case 38
Case 38